CloudFormation
Udemy - AWS CloudFormation Master Class v2 [2022]
Getting Started
Both JSON and YAML can be used with CloudFormation.
Prefer YAML as JSON is difficult to read/write for CFN templates.
YAML Supports
- Key-value pairs
- Nested Objects
- Arrays
- Multi Line Strings
- Comments
Use https://www.json2yaml.com/ for converting JSON to YAML
Example:
JSON
{
"course":"AWS Lambda",
"instructor":"Stephane Maarek",
"instructor-full":{
"first-name":"Stephane",
"last-name":"Maarek",
"awesomeness-level":9000
},
"sections-list":[
"Introduction",
"Deploying your first function",
"Learning AWS Lambda in depth",
"Real world examples"
],
"lectures":[
{
"lecture-id":1,
"lecture-name":"intro",
"lecture-length":"5:03"
},
{
"lecture-id":2,
"lecture-name":"aws lambda",
"lecture-length":"10:47"
}
]
}
YAML Equivalent
course: AWS Lambda
instructor: Stephane Maarek
instructor-full:
first-name: Stephane
last-name: Maarek
awesomeness-level: 9000
sections-list:
- Introduction
- Deploying your first function
- Learning AWS Lambda in depth
- Real world examples
lectures:
- lecture-id: 1
lecture-name: intro
lecture-length: '5:03'
- lecture-id: 2
lecture-name: aws lambda
lecture-length: '10:47'
Create/Update/Delete S3 Bucket using CloudFormation
YAML file for creating a S3 bucket with default properties:
Resources:
MyS3Bucket:
Type: AWS::S3::Bucket
Properties: {}
Equivalent JSON
{
"Resources": {
"MyS3Bucket": {
"Type": "AWS::S3::Bucket",
"Properties": {}
}
}
}
YAML file for creating a S3 bucket with AccessControl specified:
Resources:
MyS3Bucket:
Type: AWS::S3::Bucket
Properties:
AccessControl: PublicRead
Equivalent JSON
{
"Resources": {
"MyS3Bucket": {
"Type": "AWS::S3::Bucket",
"Properties": {
"AccessControl": "PublicRead"
}
}
}
}
Cloudformation Update Behavior
Cloudformation updates resources based on differences between what you submit and the stack’s current template.
Which method CFN uses depends on which property you update for a resource
- Update with No Interruption
- Without disrupting resources’ operation and without changing physical ID.
- Eg: updating the IAM instance profile (IamInstanceProfile) of an EC2 instance
- Update with some interruption
- Eg. updating an EC2 instance (InstanceType) from t2.micro to t2.large
- Replacement
- Recreating the resource with new physical ID
- Creates the new resource, change references from other resources to the new resource, then deletes the old resource
- Eg. updating an RDS DB Instance availability zone (AvailabilityZone)
Examples of update behavior with S3:
- Updates with no interruption (adding AccessControl)
- Replacement Updates (updating the name of the bucket)
The CloudFormation documentation also shows which property does what type of update
CloudFormation S3 Bucket Delete Behavior
You can’t delete a non-empty S3 bucket
To delete a non-empty S3 bucket, you must first delete all the objects inside it
CloudFormation Template Options
9 Parameters common to any CFN template
- Tags
- Permissions
- Notification Options
- Timeout
- Rollback on Failure
- Rollback Configuration (Monitoring time and CloudWatch Alarm)
- Stack Policy
- Termination Protection
- Quick-start link
We’ll discuss these in depth later in the course.
CloudFormation Building Blocks
Template Components
- AWSTemplateFormatVersion - identifies the capabilities of the template
- Description - comments about the template
- Transform - specifies one or more macros used to process the template
- Metadata
- Resources - your AWS resources declared in the template (MANDATORY)
- Parameters - the dynamic inputs for your template
- Mappings - the static variables for your template
- Outputs - References to what have been created
- Conditionals - List of conditions to perform resource creation
- Rules - validate a parameter during stack creation/update
Template Helpers
- References
- Functions
Deploying CloudFormation Templates
Automated way of deploying - use AWS CLI or a Continuous Delivery (CD) tool
CloudFormation Parameters
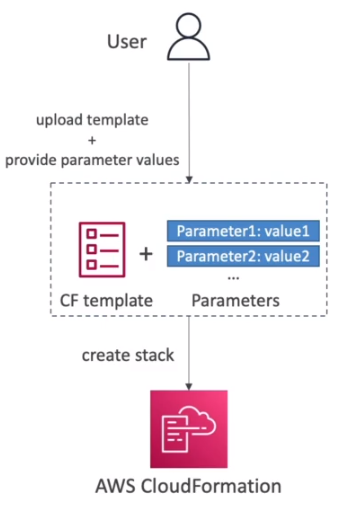
The What:
- Parameters are a way to provide inputs to your AWS CloudFormation template.
The Why:
- You want to reuse your templates across the company
- Some inputs can not be determined ahead of time
The When:
- If the CloudFormation resource configuration is likely to change in the future, make it a parameter. That way, you won’t have to re-upload a template to change its content.
Advantages:
- Extremely powerful
- Controlled
- Thanks to types, can prevent errors from happening in templates
- Can be cross-validated using Rules