Techniques to Learn Quicker and Faster
Author: Alex Brogan
Source (Twitter Threads):
- https://mobile.twitter.com/_alexbrogan/status/1512830220906151942
- https://mobile.twitter.com/_alexbrogan/status/1509206345697927170
Learn Quicker (DASCET)
- Deliberate Practice
- Deliberate practice involves focused attention on the micro-components of a skill, specific goals, and feedback on performance from an expert.
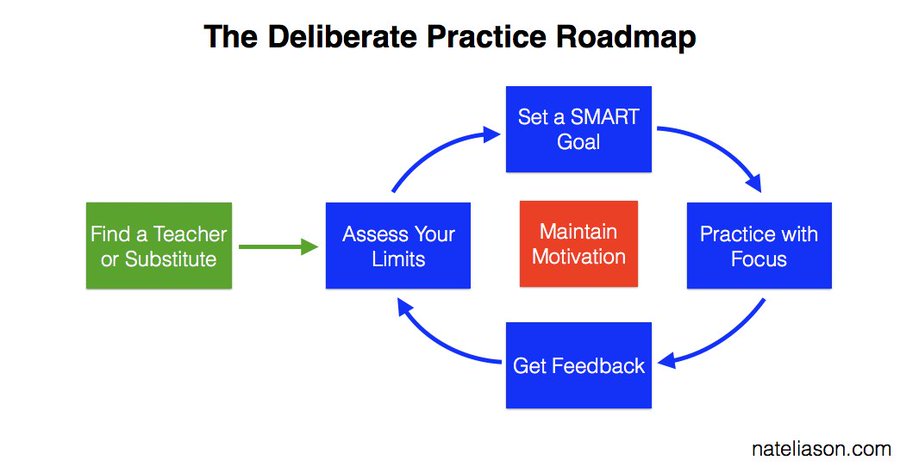
- The ADEPT Method
- A method to teach yourself a difficult idea, or explain one to others.
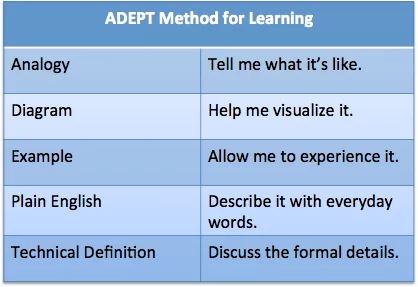
- Spaced Repetition
- Memories weaken over time.
- Combat this through spaced repetition: repeated exposure to the information to be learned over time.
- Chunking
- The process of taking individual pieces of information and grouping them into larger units to make them easier to remember.

- Elaborative Interrogation
- Involves generating an explanation for why an explicitly stated fact or concept is true.
- It’s asking yourself questions about how and why things work, and then producing the answers to these questions.
- Learning the “Why” aids retention significantly.
- The Textbook Method
- Write your own textbook chapter on a topic.
- It requires a deep understanding of the concepts and how they fit together.
- You’re forced to be consise and to create a clear mental structure of the topic.
- There’s no hiding behind knowledge gaps.
Learn Faster (PI OR QFS)
- Project-Based Learning
- Ask, what project can you do to learn the skill or topic of knowledge?
- Immersive Learning
- Involves surrounding yourself directly in the environment where the skill will be used. Eg: Moving to a country to learn the native language.
- The Overkill Approach
- Involves putting yourself in a high-demand environment, so you’re unlikely to miss important feedback lessons.
- More feedback = more learning.
- Retrieval
- The hard thing to do when learning is actively trying to recall without re-reading or viewing.
- The Question-Book Method
- Rephrase notes as questions to be answered later—this engages the retrieval muscle.
- When reading a book, restate the big idea of a chapter or section as a question.
- The Feynman Technique
- STEP 1 - Pick and study a topic
- STEP 2 - Explain the topic to someone, like a child, who is unfamiliar with the topic
- STEP 3 - Identify any gaps in your understanding
- STEP 4 - Review and Simplify! Convey it to others. Test-and-learn. Iterate and refine your story or narrative accordingly.
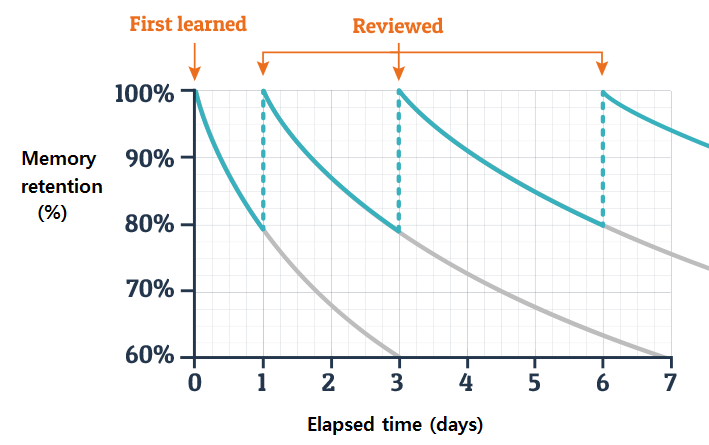
- Spaced Repetition
- Spreading learning sessions over more intervals over longer periods of time.
- If you have 10 hours to learn something, it makes more sense to spend 10 days studying one hour each than to spend 10 hours studying in one burst.
- Repeat to remember.
Speed Reading
- https://tim.blog/2009/07/30/speed-reading-and-accelerated-learning/
- https://tim.blog/2015/06/09/speed-reading/